|
| credits: tdwi.org |
“A huge amount
of data keeps coming in exponentially from a variety of sources”
The above
statement pretty much sums up the definition of Big Data very concisely.
Let’s find the
THREE Vs in that statement:
“huge amount of
data” = Volume
“coming
exponentially” = Velocity
“variety of
sources” = Variety
Volume, Velocity,
and Variety are the three factors that make Big Data so complex to store and
process.
So, coming to our
last question where and how we are supposed to store such a big amount of data
for processing?
Data
Compression and encoding
“Reduce the size
of data without changing its fundamental properties”
Encode the data
using fewer bits from the original data size, which can then be decoded and
retrieved during the time of access.
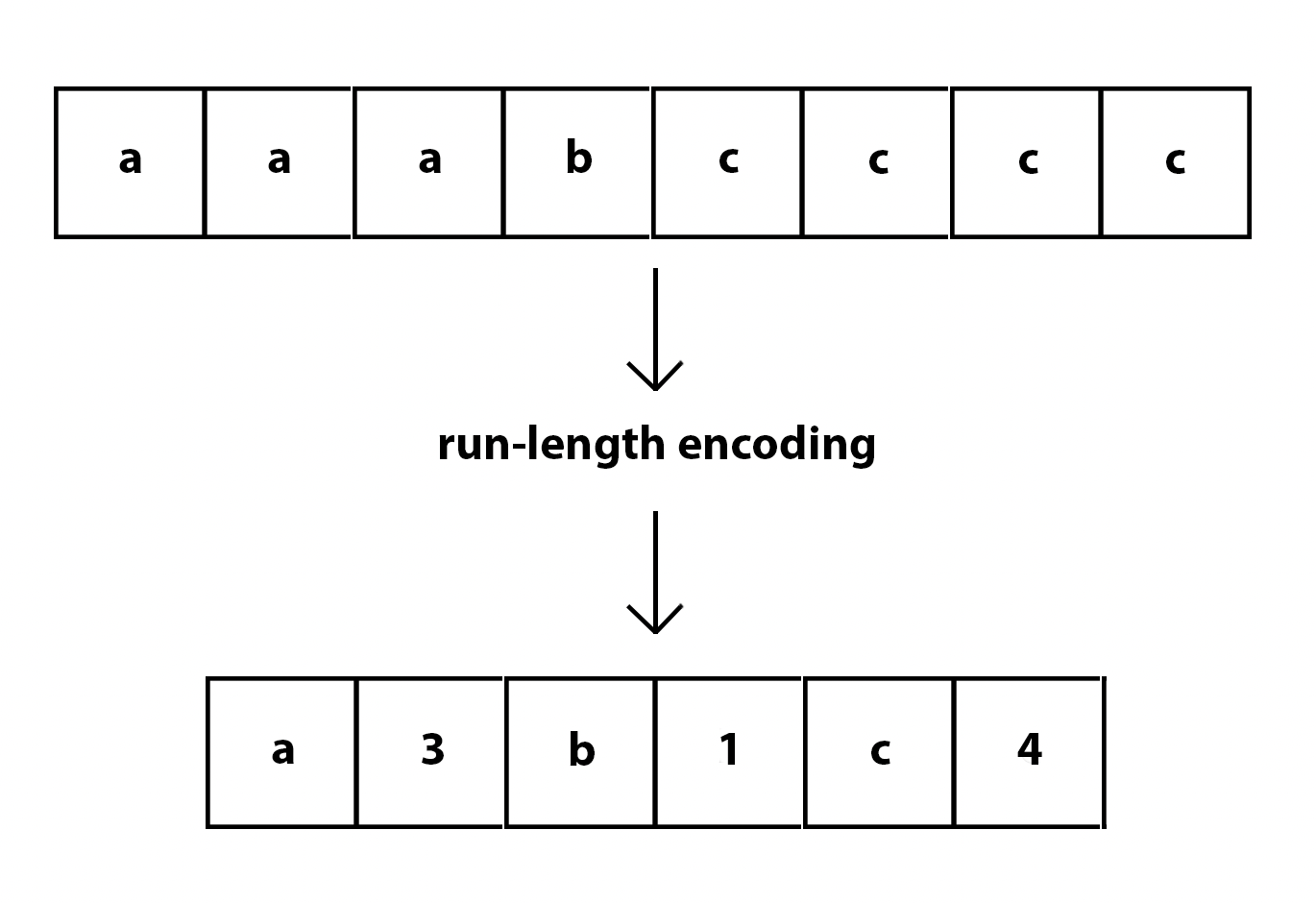
The above image is
an example of Run Length encoding that replaces consecutive occurrences of the
same data value with a single value. It is one of the many encoding techniques
that is used to reduce storage
space and improve data transfer efficiency.
Where to store Big Data?
Big data is stored
in specialized data storage systems and platforms designed to handle the
volume, variety, and velocity of large datasets. Selecting a storage system
depends on the type of data you’re dealing with. Examples are:
Distributes
File Systems like HDFS
which stores and manages data across multiple machines in a distributed
environment.
NoSQL Databases which are highly scalable and can handle
diverse data (text, video, audio, images),
Data warehouses which primarily store structured data in
centralized repositories
Object Storage primarily stores unstructured data such as
images, videos, documents, and log files in a highly scalable and durable
environment.
Data Lake stores raw and unprocessed data in
centralized repositories. It contains structured, semi-structured, and
unstructured data.
All these storage
systems above can be used for different purposes like Batch Processing and
Analytics, Storing and retrieving user-generated content, Business Intelligence
and Analytics, Data Archiving and Backup for long-term storage and disaster
recovery, Data Exploration and Advanced Analytics for exploratory analysis,
machine learning, and predictive modeling respectively.